Serialization of Ink
The Ink Serialization module provides algorithms for encoding and decoding ink content and related meta data. These algorithms are optimized to work with the Universal Ink Model.
The algorithms support the following features:
- Fast encoding and decoding
- Compact file size
- Portability across operating systems and devices
- Binary representation that can be embedded in different container formats
To read more about the encoding scheme, click here.
Handling model
The following illustrates how to manage the data used within the Universal Ink Model. Within the ink model, several data repositories -- as well as the ink tree, the views, and knowledge graph -- need to be managed if the information is required for the use case.
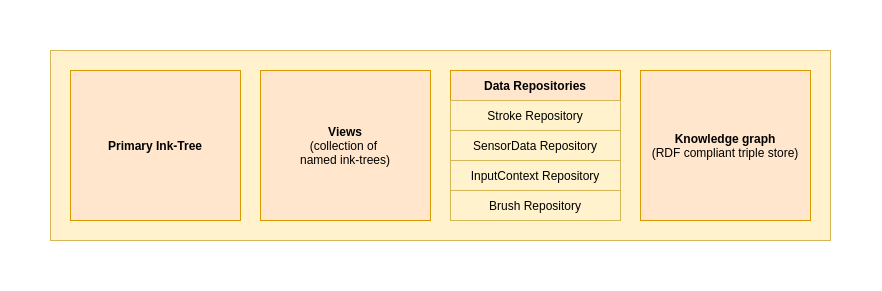
Ink Model
The first step is to create an instance of the InkModel.
- Kotlin
- C#
- JavaScript
inkModel = InkModel()
public class Serializer
{
...
public void Init()
{
InkDocument = new InkModel();
InkDocument.InkTree.Root = new StrokeGroupNode(Identifier.FromNewGuid());
}
class DataModel {
constructor() {
this.inkModel = new InkModel();
this.repository = new DataRepository();
this.manipulationsContext = new SpatialContext();
}
...
Input Context Repository
The input context describes capturing the sensor data. This information needs to be added by the application, but -- depending on the use case of the application -- it may not be needed. Storage of the sensor data is also optional.
The following sections provide some examples of how the context can be defined.
Environment
The environment in which the sensor data has been produced (the operating system, etc.) can be defined as follows:
- Kotlin
- C#
import com.wacom.ink.format.input.*
...
// Initialize environment
environment = Environment()
environment.putProperty("os.name", "android")
environment.putProperty("os.version.name", Build.VERSION.CODENAME)
environment.putProperty("os.version.code", Build.VERSION.SDK_INT.toString())
environment.putProperty("os.version.incremental", Build.VERSION.INCREMENTAL)
environment.putProperty("os.version.release", Build.VERSION.RELEASE)
environment.putProperty("wacom.ink.sdk.name", activity.getString(R.string.sdk_name))
environment.putProperty("wacom.ink.sdk.version", activity.getString(R.string.sdk_version))
// Init environment
mEnvironment.Properties["os.name"] = m_eas.OperatingSystem;
mEnvironment.Properties["os.version.code"] = System.Environment.OSVersion.Version.ToString();
mEnvironment.Seal();
InkInputProvider
The ink input provider represents the generic input data source. It identifies how the data has been generated (using touch input, mouse, stylus, hardware controller, etc). For each platform and device, the application has to decide which input device is used within the application and serialize within the ink model.
- Kotlin
- C#
- JavaScript
import com.wacom.ink.format.input.*
...
val toolType = when (event.getToolType(0)) {
MotionEvent.TOOL_TYPE_STYLUS -> InkInputType.PEN
MotionEvent.TOOL_TYPE_FINGER -> InkInputType.TOUCH
MotionEvent.TOOL_TYPE_MOUSE -> InkInputType.MOUSE
else -> InkInputType.PEN
}
val provider = InkInputProvider(toolType)
TBD
TBD
Input Device
The input device which has been used to produce the sensor data. Depending on the platform, there may be several input devices available. Some tablets already have a stylus, or one is available as an accessory. The following properties can be collected as provided, for instance by the platform itself:
- Kotlin
- C#
- JavaScript
import com.wacom.ink.format.input.*
...
// Initialize InputDevice
inputDevice = InputDevice()
inputDevice.putProperty("dev.id", Build.ID)
inputDevice.putProperty("dev.manufacturer", Build.MANUFACTURER)
inputDevice.putProperty("dev.brand", Build.BRAND)
inputDevice.putProperty("dev.model", Build.MODEL)
inputDevice.putProperty("dev.board", Build.BOARD)
inputDevice.putProperty("dev.hardware", Build.HARDWARE)
inputDevice.putProperty("dev.codename", Build.DEVICE)
inputDevice.putProperty("dev.display", Build.DISPLAY)
...
{
InputDevice inputDevice = new InputDevice();
inputDevice.Properties["dev.name"] = System.Environment.MachineName;
inputDevice.Seal();
Identifier inputDeviceId = inputDevice.Id;
bool res = InkDocument.InputConfiguration.Devices.Any((device) => device.Id == inputDeviceId);
if (!res)
{
InkDocument.InputConfiguration.Devices.Add(inputDevice);
}
return inputDevice;
}
/**
* Creates default input device instance, based on system information
*
* @param {Properties} envProps User defined env properties, like app.id for example
* @return {InkInput.InputDevice} default instance
*/
static async createInstance(envProps) {
let device = new this(...Array.from(arguments).slice(1));
if (typeof sysInfo == "undefined")
device.props["dev.graphics.resolution"] = `${screen.width}x${screen.height}`;
else {
let system = await sysInfo.system();
let cpu = await sysInfo.cpu();
let graphics = await sysInfo.graphics();
let display = graphics.displays.filter(d => d.main)[0];
let adapter = graphics.controllers[0];
device.props["dev.id"] = system.uuid.toLowerCase();
device.props["dev.manufacturer"] = system.manufacturer;
device.props["dev.model"] = system.model;
device.props["dev.cpu"] = `${cpu.manufacturer} ${cpu.brand} ${cpu.speed} - ${cpu.cores} core(s)`;
device.props["dev.graphics.display"] = `${display.model} ${display.currentResX}x${display.currentResY} (${display.pixeldepth} bit)`;
device.props["dev.graphics.adapter"] = `${adapter.model} ${adapter.vram} GB`;
}
device.environment = await Environment.createInstance(envProps);
return device;
}
...
let device = await InputDevice.createInstance({"app.id": "will3-sdk-for-ink-web-demo", "app.version": "1.0.0"});
SensorContext
The sensor context is a unique combination of sensor channel contexts, used for capturing the digital ink input. This information can be beneficial if the sensor data is used within a machine learning context where data needs to be normalized.
- Kotlin
- C#
// Define which channels are used for sensor data collection
var inkSensorTypes = listOf(InkSensorType.X, InkSensorType.Y, InkSensorType.TIMESTAMP)
...
// Register the channels which are used for sensor data collection
val channels = registerChannels(inkSensorTypeUris)
// Define the context for the sensor channels
val sensorChannelsContext = SensorChannelsContext(provider.id, inputDevice.id, channels)
val sensorContext = SensorContext()
sensorContext.addSensorChannelsContext(sensorChannelsContext)
// Maintain a map of contexts by id
sensorContexts[sensorContext.id] = sensorContext
// Input context is combining environment and sensor context
val inputContext = InputContext(environment.id, sensorContext.id)
// Maintain a map of input context
inputContexts[inputContext.id] = inputContext
inputProviderToInputContextMapping[provider.id] = inputContext.id
...
private fun registerChannels(inkSensorTypeUris: List<String>): MutableList<SensorChannel> {
val precision = 2
val channels = mutableListOf<SensorChannel>()
val dimensions = getScreenDimensions()
for (type in inkSensorTypeUris) {
val channel = when (type) {
InkSensorType.X -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.X,
InkSensorMetricType.LENGTH,
ScalarUnit.INCH,
0.0f,
dimensions.x,
precision
)
InkSensorType.Y -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.Y,
InkSensorMetricType.LENGTH,
ScalarUnit.INCH,
0.0f,
dimensions.y,
precision
)
InkSensorType.Z -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.Z,
InkSensorMetricType.LENGTH,
ScalarUnit.DIP,
0.0f,
0.0f,
precision
)
InkSensorType.TIMESTAMP -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.TIMESTAMP,
InkSensorMetricType.TIME,
ScalarUnit.MILLISECOND,
0.0f,
0.0f,
precision
)
InkSensorType.PRESSURE -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.PRESSURE,
InkSensorMetricType.NORMALIZED,
ScalarUnit.NORMALIZED,
0.0f,
1.0f,
precision
)
InkSensorType.RADIUS_X -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.RADIUS_X,
InkSensorMetricType.LENGTH,
ScalarUnit.DIP,
0.0f,
0.0f,
precision
)
InkSensorType.RADIUS_Y -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.RADIUS_Y,
InkSensorMetricType.LENGTH,
ScalarUnit.DIP,
0.0f,
0.0f,
precision
)
InkSensorType.ALTITUDE -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.ALTITUDE,
InkSensorMetricType.ANGLE,
ScalarUnit.RADIAN,
0.0f,
(Math.PI/2).toFloat(),
precision
)
InkSensorType.AZIMUTH -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.AZIMUTH,
InkSensorMetricType.ANGLE,
ScalarUnit.RADIAN,
-(Math.PI/2).toFloat(),
(Math.PI/2).toFloat(),
precision
)
InkSensorType.ROTATION -> SensorChannel(
InkSensorType.ROTATION,
InkSensorMetricType.ANGLE,
ScalarUnit.RADIAN,
0.0f,
0.0f,
precision
)
else -> {
throw Exception("Unknown channel type.")
}
}
channels.add(channel)
}
return channels
// Init sensor channels contexts
SensorChannelsContext mouseSensorChannelsContext = SensorChannelsContext.CreateDefault(mouseInputProvider, m_currentInputDevice); //new SensorChannelsContext(mouseInputProvider, m_currentInputDevice, m_sensorChannels);
SensorChannelsContext touchSensorChannelsContext = SensorChannelsContext.CreateDefault(touchInputProvider, m_currentInputDevice); //new SensorChannelsContext(touchInputProvider, m_currentInputDevice, m_sensorChannels);
SensorChannelsContext penSensorChannelsContext = SensorChannelsContext.CreateDefault(penInputProvider, m_currentInputDevice); //new SensorChannelsContext(penInputProvider, m_currentInputDevice, m_sensorChannels);
// Cache sensor channels contexts
m_sensorChannelsContexts.Add(mouseSensorChannelsContext.Id, mouseSensorChannelsContext);
m_sensorChannelsContexts.Add(touchSensorChannelsContext.Id, touchSensorChannelsContext);
m_sensorChannelsContexts.Add(penSensorChannelsContext.Id, penSensorChannelsContext);
SensorData Repository
To track the sensor data it is important to know the InkInputProvider on all platforms and this can be inferred from the events.
Moreover, the rendering behavior differs for instance between touch and stylus input providers.
- Kotlin
- C#
- JavaScript
...
val touchChannels = listOf(InkSensorType.X, InkSensorType.Y, InkSensorType.TIMESTAMP)
val penChannels = listOf(InkSensorType.X, InkSensorType.Y, InkSensorType.TIMESTAMP,
InkSensorType.PRESSURE, InkSensorType.ALTITUDE, InkSensorType.AZIMUTH)
...
fun createSensorData(event: MotionEvent): Pair<SensorData, List<SensorChannel>> {
// MotionEvent tool type helps to decide on the appropriate ink input provider
val toolType = when (event.getToolType(0)) {
MotionEvent.TOOL_TYPE_STYLUS -> InkInputType.PEN
MotionEvent.TOOL_TYPE_FINGER -> InkInputType.TOUCH
MotionEvent.TOOL_TYPE_MOUSE -> InkInputType.MOUSE
else -> InkInputType.PEN
}
var provider: InkInputProvider? = null
// First, check if exist an input provider of the desired type
for ((_, existingProvider) in inputProviders) {
existingProvider.type == toolType
provider = existingProvider
break
}
if (provider == null) {
provider = InkInputProvider(toolType)
// It is possible to add custom define properties to the input provider
// for example PenID in case exists
if (toolType == InkInputType.PEN) {
provider.putProperty("penType", "s-pen") // Assuming using Samsung S Pen
}
}
var inputContextId = if (!inputProviders.containsKey(provider.id)) {
inputProviders[provider.id] = provider
// Build the list of channels
val channels = registerChannels(if (toolType == InkInputType.PEN) penChannels else touchChannels)
channelsForInput.put(provider.id, channels)
val sensorChannelsContext = SensorChannelsContext(
provider.id, // Reference to input input provider
inputDevice.id, // Reference to input device
channels) // Channels for the registered channels
val sensorContext = SensorContext()
sensorContext.addSensorChannelsContext(sensorChannelsContext)
sensorContexts[sensorContext.id] = sensorContext
val inputContext = InputContext(
environment.id, // Reference to environment
sensorContext.id) // Reference to sensor context
inputContexts[inputContext.id] = inputContext
inputProviderToInputContextMapping[provider.id] = inputContext.id
inputContext.id
} else {
val provider = inputProviders[provider.id]!!
inputProviderToInputContextMapping[provider.id]!!
}
var channelList: List<SensorChannel>? = null
for ((id, channels) in channelsForInput) {
if (provider.id == id) {
channelList = channels
}
}
if (channelList == null) {
channelList = listOf() // empty list to avoid null pointer exceptions
}
// Create the SensorData object with a new unique ID and its input context reference id
return Pair<SensorData,
List<SensorChannel>>(SensorData(UUID.randomUUID().toString(), inputContextId, InkState.PLANE),
channelList)
}
override fun onEvent(pointerData: PointerData, inkToolType: InkInputType) {
when (pointerData.phase) {
// Set the appropriate input provider
Phase.BEGIN -> {
if ((inputProvider.type != inkToolType)) {
inputProvider = InkInputProvider(inkToolType)
}
}
// Adding sensor data
Phase.UPDATE, Phase.END -> {
sensorData.add(sensorChannels[InkSensorType.X]!!, pointerData.x)
sensorData.add(sensorChannels[InkSensorType.Y]!!, pointerData.y)
sensorData.addTimestamp(sensorChannels[InkSensorType.TIMESTAMP]!!,
pointerData.timestamp)
}
}
}
...
}
public Identifier AddSensorData(PointerDeviceType deviceType, List<PointerData> pointerDataList)
{
Identifier inputContextId = m_deviceTypeMap[deviceType];
InputContext inputContext = m_inputContexts[inputContextId];
SensorContext sensorContext = m_sensorContexts[inputContext.SensorContextId];
// Create sensor data using the input context
SensorData sensorData = new SensorData(
Identifier.FromNewGuid(),
inputContext.Id,
InkState.Plane);
PopulateSensorData(sensorData, sensorContext, pointerDataList);
m_sensorDataMap.TryAdd(sensorData.Id, sensorData);
return sensorData.Id;
}
...
/// <summary>
/// Make the current stroke permanent
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>Copies the output of the render pipeline from InkBuilder to dry strokes</remarks>
public override void StoreCurrentStroke(PointerDeviceType deviceType)
{
var allData = RasterInkBuilder.SplineInterpolator.AllData;
var points = new List<float>();
if (allData != null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < allData.Count; i++)
{
points.Add(allData[i]);
}
if (points.Count > 0)
{
var dryStroke = new RasterInkStroke(RasterInkBuilder,
deviceType,
points,
m_startRandomSeed,
CreateSerializationBrush($"will://examples/brushes/{Guid.NewGuid().ToString()}"),
mStrokeConstants.Clone(),
mSerializer.AddSensorData(deviceType, InkBuilder.GetPointerDataList()));
m_dryStrokes.Add(dryStroke);
}
}
}
add(stroke) {
this.manipulationsContext.add(stroke);
return this.inkModel.addPath(stroke);
}
...
begin(sensorPoint) {
if (this.forward) return this.inkCanvasRaster.begin(sensorPoint);
this.reset(sensorPoint);
this.builder.add(sensorPoint);
this.builder.build();
}
move(sensorPoint) {
if (this.forward) return this.inkCanvasRaster.move(sensorPoint);
if (app.downsampling && this.requested) {
this.builder.ignore(sensorPoint);
return;
}
this.builder.add(sensorPoint);
if (!this.requested) {
this.requested = true;
this.builder.build();
requestAnimationFrame(() => (this.requested = false));
}
}
end(sensorPoint) {
if (this.forward) return this.inkCanvasRaster.end(sensorPoint);
this.builder.add(sensorPoint);
this.builder.build();
}
Stroke Repository
The visual output of the rendering pipeline must be stored as well, as this is a crucial part of the Universal Ink Model. Here the following structures need to be added:
- Kotlin
- C#
- JavaScript
import com.wacom.ink.format.rendering.PathPointProperties
import com.wacom.ink.format.rendering.Style
import com.wacom.ink.format.tree.data.Stroke
import com.wacom.ink.format.tree.nodes.StrokeNode
import com.wacom.ink.model.IdentifiableImpl
...
fun surfaceTouch(event: MotionEvent) {
...
if ((pointerData.phase == Phase.END) &&
(rasterInkBuilder.splineProducer.allData != null)) {
addStroke(event)
}
...
}
...
private fun addStroke(event: MotionEvent) {
// Adding the style
val style = Style(
rasterTool.uri(), // Style URI
1, // Particle random seed
props = PathPointProperties( // Coloring path properties
red = defaults.red,
green = defaults.green,
blue = defaults.blue,
alpha = defaults.alpha
),
renderModeUri = rasterTool.getBlendMode().name
)
// Adding stroke to the Stroke Repository
val path = Stroke(
IdentifiableImpl.generateUUID(), // Generated UUID
rasterInkBuilder.splineProducer.allData!!.copy(), // Spline
style // Style
)
// Adding a node to the Ink tree
val node = StrokeNode(IdentifiableImpl.generateUUID(),
path)
...
strokeNodeList.add(node)
}
private void EncodeStrokeCommon(Identifier id, Spline spline , PathPointLayout layout, Identifier sensorDataId, Style style)
{
Stroke stroke = new Stroke(
id,
spline.Clone(),
style,
layout,
sensorDataId);
StrokeNode strokeNode = new StrokeNode(Identifier.FromNewGuid(), stroke);
InkDocument.InkTree.Root.Add(strokeNode);
if (sensorDataId != Identifier.Empty)
{
SensorData sensorData = m_sensorDataMap[sensorDataId];
AddSensorDataToModel(sensorData);
}
}
draw(pathPart) {
this.drawPath(pathPart);
if (pathPart.phase == InkBuilder.Phase.END) {
if (this.strokeRenderer) {
let stroke = this.strokeRenderer.toStroke(this.builder);
this.dataModel.add(stroke)
}
}
}
Brush Repository
As we need to ensure that the ink strokes can be rendered on a different platform or application, every brush needs to be embedded.
- Kotlin
- C#
fun setTool(view: View, tool: Tool) {
drawingTool = tool
if (drawingTool is VectorTool) {
vectorDrawingView.setTool(drawingTool as VectorTool)
} else {
val dt = drawingTool as RasterTool
val brush = dt.brush
if (inkModel.brushRepository.getBrush(brush.name) == null) {
// Adding a raster brush if it is not within the repository yet
inkModel.brushRepository.addRasterBrush(brush as RasterBrush)
}
rasterDrawingSurface.setTool(dt)
}
highlightTool(view)
}
private void AddRasterBrushToInkDoc(PointerDeviceType deviceType, RasterBrush rasterBrush,
Style rasterStyle, StrokeConstants strokeConstants,
uint startRandomSeed)
{
rasterStyle.RenderModeUri = $"will3://rendering//{deviceType.ToString()}";
if (!InkDocument.Brushes.TryGetBrush(rasterBrush.Name, out Brush foundBrush))
{
InkDocument.Brushes.AddRasterBrush(rasterBrush);
}
}
private void AddVectorBrushToInkDoc(string pointerDeviceType, Wacom.Ink.Serialization.Model.VectorBrush vectorBrush, Style style)
{
style.RenderModeUri = $"will3://rendering//{pointerDeviceType}";
if (!InkDocument.Brushes.TryGetBrush(vectorBrush.Name, out Brush foundBrush))
{
InkDocument.Brushes.AddVectorBrush(vectorBrush);
}
}
Persistence
In order to persist the Ink Model and share it across platforms it needs to be encoded in a data stream.
Encoding
The model will be encoded using binary representation, more details here.
- Kotlin
- C#
- JavaScript
try {
val file = File(filePath)
fileOutputStream = FileOutputStream(file)
// Serialize encoded ink model to an output stream
Will3Codec.encode(inkModel, fileOutputStream)
} catch (e: Exception){
e.printStackTrace()
} finally {
fileOutputStream?.close()
}
StorageFile file = await savePicker.PickSaveFileAsync();
if (file != null)
{
// Prevent updates to the remote version of the file until we finish making changes and call CompleteUpdatesAsync.
CachedFileManager.DeferUpdates(file);
// Write to file
await FileIO.WriteBytesAsync(file, Will3Codec.Encode(m_renderer.StrokeHandler.Serialize()));
// Let Windows know that we're finished changing the file so the other app can update the remote version of the file.
// Completing updates may require Windows to ask for user input.
FileUpdateStatus status = await CachedFileManager.CompleteUpdatesAsync(file);
if (status != FileUpdateStatus.Complete)
{
MessageDialog md = new MessageDialog("File could not be saved!", "Error saving file");
await md.ShowAsync();
}
}
async encode() {
return await this.codec.encodeInkModel(this.dataModel.inkModel);
}
...
async save() {
let buffer = await this.encode();
fsx.saveAs(buffer, "ink.uim", "application/vnd.wacom-ink.model");
}
Decoding
In order to decode the stream, the encoded data needs to be passed to the decoder function. As the version number of the data format is encoded within the RIFF header, the appropriate version of the content parser will be chosen automatically.
- Kotlin
- C#
- JavaScript
// Loading file stream from path
val fileInputStream = FileInputStream(File(path))
// Read bytes array with UIM content
val bytes = fileInputStream.readBytes()
// Using the codec decoder to de-serialize the InkModel
val inkModel = Will3Codec.decode(bytes)
StorageFile file = await picker.PickSingleFileAsync();
if (file != null)
{
try
{
IBuffer fileBuffer = await FileIO.ReadBufferAsync(file);
var inkDocument = Will3Codec.Decode(fileBuffer.ToArray());
...
async openFile(buffer) {
let inkModel = this.codec.decodeInkModel(buffer);
...